الگوریتم کارگر برای برش کمینه — راهنمای کاربردی
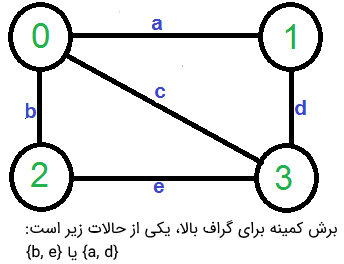
یک گراف غیر جهتدار و بدون وزن داده شده است. هدف پیدا کردن «برش کمینه» (Minimum Cut) است. منظور از برش کمینه، پیدا کردن کمترین تعداد یالهایی است که گراف را به دو مولفه میشکند. گراف ورودی ممکن است دارای یالهای موازی باشد. برای مثال، گراف زیر را در نظر بگیرید. برش کمینه دارای ۲ یال است.
یک راهکار ساده، استفاده از «الگوریتم برش s-t بیشینه جریان» (Max-Flow Based s-t Cut Algorithm) برای پیدا کردن برش کمینه است. هر جفت از رأسها را میتوان به عنوان مبدا (Source | s) و مقصد (Sink | t) در نظر گرفت و الگوریتم برش s-t را برای پیدا کردن برش s-t فراخوانی کرد. این الگوریتم، همه برشهای s-t کمینه را باز میگرداند. بهترین پیچیدگی زمانی این الگوریتم از درجه (O(V5 برای گراف است. دلیل این امر آن است که V2 جفت حالت امکانپذیر وجود دارد و الگوریتم برش s-t برای یک جفت، از (O(V*E زمان میبرد و داریم که (E = O(V2.
در ادامه، الگوریتم کارگر ساده برای هدف بیان شده در ای مسئله، ارائه شده است. الگوریتم کارگر زیر را میتوان با درجه زمانی (O(E) = O(V2 پیادهسازی کرد.
- گراف contracted را با نام CG به عنوان یک کپی از گراف اصلی مقداردهی اولیه کن.
- تا هنگامی که بیش از ۲ راس وجود ندارد:
- یک یال تصادفی (u, v) را در گراف contracted انتخاب کن.
- u و v را در گراف contracted در یک راس با یکدیگر ادغام کن (گراف contracted را به روز رسانی کن).
- خود-حلقهها را حذف کن
- برش ارائه شده توسط دو رأس را در خروجی بازگردان.
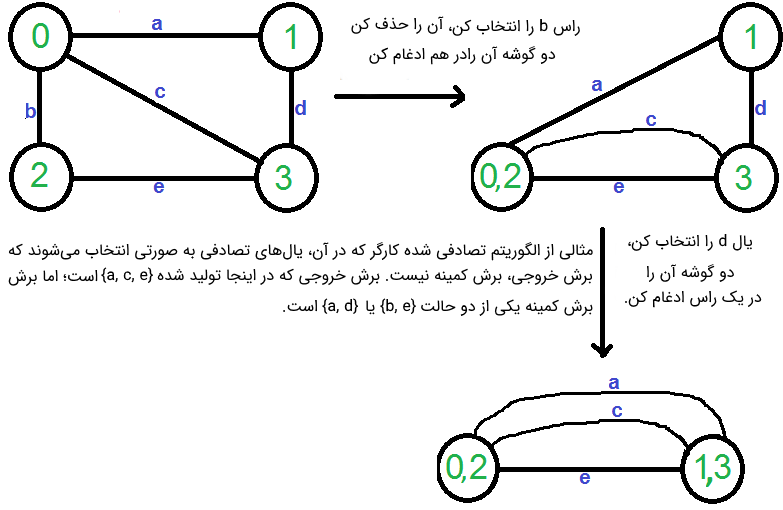
در ادامه، الگوریتم بالا از طریق یک مثال داده شده مورد بررسی قرار خواهد گرفت. ابتدا یال a که رأسهای ۰ و ۱ را متصل میکند، به صورت تصادفی انتخاب میشود. این یال حذف میشود و گراف contract میشود (ترکیب رأسهای ۰ و ۱). گراف زیر در نتیجه حاصل میشود.

در ادامه، فرض میشود که یال تصادفی انتخاب شده بعدی، یال d است. این یال حذف میشود و رأسهای (۱و۰) و ۳ ادغام میشوند.
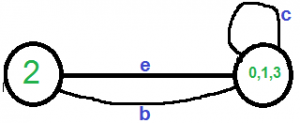
اکنون، نیاز به حذف حلقه خودتکرار در گراف است. بنابراین، رأس c حذف خواهد شد.
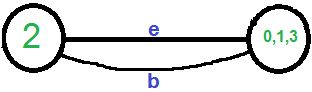
اکنون، گراف دارای دو رأس است. بنابراین الگوریتم متوقف میشود. تعداد یالهای موجود در گراف حاصل شده، برش تولید شده به وسیله الگوریتم کارگر هستند. الگوریتم کارگر، یک الگوریتم «مونت کارلو» (Monte Carlo) است و برش تولید شده توسط آن ممکن است کمینه نباشد. برای مثال، نمودار زیر نشان میدهد که ترتیب متفاوتی از انتخاب یالهای تصادفی، منجر به تولید یک برش کمینه با اندازه ۳ خواهد شد.
درادامه، پیادهسازی الگوریتم کارگر به شیوه ارائه شده در بالا، در زبان برنامهنویسی «سیپلاسپلاس» (++C) انجام شده است.گراف ورودی به عنوان مجموعهای از یالها و ساختار مجموعههای مجزا (Union-Find Data Structure) به منظور ردیابی مولفهها، ارائه شده است.
پیادهسازی الگوریتم کارگر در زبان C
// Karger's algorithm to find Minimum Cut in an
// undirected, unweighted and connected graph.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
// a structure to represent a unweighted edge in graph
struct Edge
{
int src, dest;
};
// a structure to represent a connected, undirected
// and unweighted graph as a collection of edges.
struct Graph
{
// V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges
int V, E;
// graph is represented as an array of edges.
// Since the graph is undirected, the edge
// from src to dest is also edge from dest
// to src. Both are counted as 1 edge here.
Edge* edge;
};
// A structure to represent a subset for union-find
struct subset
{
int parent;
int rank;
};
// Function prototypes for union-find (These functions are defined
// after kargerMinCut() )
int find(struct subset subsets[], int i);
void Union(struct subset subsets[], int x, int y);
// A very basic implementation of Karger's randomized
// algorithm for finding the minimum cut. Please note
// that Karger's algorithm is a Monte Carlo Randomized algo
// and the cut returned by the algorithm may not be
// minimum always
int kargerMinCut(struct Graph* graph)
{
// Get data of given graph
int V = graph->V, E = graph->E;
Edge *edge = graph->edge;
// Allocate memory for creating V subsets.
struct subset *subsets = new subset[V];
// Create V subsets with single elements
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
subsets[v].parent = v;
subsets[v].rank = 0;
}
// Initially there are V vertices in
// contracted graph
int vertices = V;
// Keep contracting vertices until there are
// ۲ vertices.
while (vertices > 2)
{
// Pick a random edge
int i = rand() % E;
// Find vertices (or sets) of two corners
// of current edge
int subset1 = find(subsets, edge[i].src);
int subset2 = find(subsets, edge[i].dest);
// If two corners belong to same subset,
// then no point considering this edge
if (subset1 == subset2)
continue;
// Else contract the edge (or combine the
// corners of edge into one vertex)
else
{
printf("Contracting edge %d-%d\n",
edge[i].src, edge[i].dest);
vertices--;
Union(subsets, subset1, subset2);
}
}
// Now we have two vertices (or subsets) left in
// the contracted graph, so count the edges between
// two components and return the count.
int cutedges = 0;
for (int i=0; i<E; i++)
{
int subset1 = find(subsets, edge[i].src);
int subset2 = find(subsets, edge[i].dest);
if (subset1 != subset2)
cutedges++;
}
return cutedges;
}
// A utility function to find set of an element i
// (uses path compression technique)
int find(struct subset subsets[], int i)
{
// find root and make root as parent of i
// (path compression)
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent =
find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
// A function that does union of two sets of x and y
// (uses union by rank)
void Union(struct subset subsets[], int x, int y)
{
int xroot = find(subsets, x);
int yroot = find(subsets, y);
// Attach smaller rank tree under root of high
// rank tree (Union by Rank)
if (subsets[xroot].rank < subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[xroot].parent = yroot;
else if (subsets[xroot].rank > subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
// If ranks are same, then make one as root and
// increment its rank by one
else
{
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
subsets[xroot].rank++;
}
}
// Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges
struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E)
{
Graph* graph = new Graph;
graph->V = V;
graph->E = E;
graph->edge = new Edge[E];
return graph;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
/* Let us create following unweighted graph
۰------۱
| \ |
| \ |
| \|
۲------۳ */
int V = 4; // Number of vertices in graph
int E = 5; // Number of edges in graph
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
// add edge 0-1
graph->edge[0].src = 0;
graph->edge[0].dest = 1;
// add edge 0-2
graph->edge[1].src = 0;
graph->edge[1].dest = 2;
// add edge 0-3
graph->edge[2].src = 0;
graph->edge[2].dest = 3;
// add edge 1-3
graph->edge[3].src = 1;
graph->edge[3].dest = 3;
// add edge 2-3
graph->edge[4].src = 2;
graph->edge[4].dest = 3;
// Use a different seed value for every run.
srand(time(NULL));
printf("\nCut found by Karger's randomized algo is %d\n",
kargerMinCut(graph));
return 0;خروجی قطعه کد بالا، به صورت زیر است.
Contracting edge 0-2
Contracting edge 0-3
Cut found by Karger's randomized algo is 2اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامهنویسی
- آموزش ساختمان دادهها
- مجموعه آموزشهای ساختمان داده و طراحی الگوریتم
- معرفی منابع آموزش ویدئویی هوش مصنوعی به زبان فارسی و انگلیسی
- زبان برنامهنویسی پایتون (Python) — از صفر تا صد
- آموزش ساختمان داده — مجموعه مقالات جامع وبلاگ فرادرس
مجموعه: برنامه نویسی, مهندسی کامپیوتر برچسب ها: Minimum Cut, Monte Carlo, الگوریتم کارگر, الگوریتم کارگر در C, محاسبه برش کمینه, مونت کارلو




 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)