برنامه بررسی دور اویلری در گراف جهت دار — راهنمای کاربری
مسیر اویلری (Eulerian Path) مسیری درگراف است که در آن، هر رأس از گراف، دقیقا یکبار مشاهده میشود. «دور اویلری» (Eulerian Circuit) یک مسیر اویلری است که با یک رأس شرع و با همان رأس نیز تمام میشود. یک گراف را گراف اویلری میگویند اگر دارای دور اویلری باشد. در این مطلب، به بررسی دور اویلری در گراف جهتدار پرداخته میشود. برای مثال، گراف زیر دارای دور اویلری {۱, ۰, ۳, ۴, ۰, ۲, ۱} است.
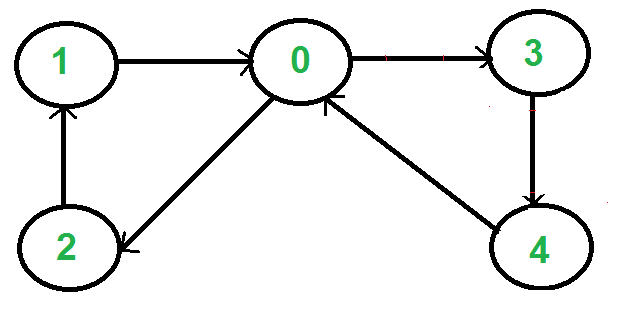
روش بررسی اویلری بودن یک گراف جهتدار
یک گراف جهتدار در صورت صدق کردن در شرطهای زیر، اویلری محسوب میشود.
- همه رأسها با درجه غیر صفر متعلق به یک مولفه قویا متصل مجرد باشند.
- درجه ورود برای هر رأس با درجه خروج برای آن رآس دقیقا برابر باشد.
میتوان یک مولفه متصل به صورت مجرد را با استفاده از «الگوریتم ساده مبتنی بر جستجوی اول عمق کساراجو» (Kosaraju’s DFS Based Simple Algorithm) شناسایی کرد. برای مقایسه درجه ورودی و خروجی، نیاز به ذخیرهسازی درجه ورودی و خروجی برای همه رأسها است. درجه خروجی را میتوان با استفاده از اندازه لیست مجاورت نیز به دست آورد. درج ورودی را میتوان با ساخت یک آرایه با اندازهای مشابه با اندازه رأسها ذخیرهسازی کرد. در ادامه، پیادهسازی رویکرد بیان شده در زبانهای برنامهنویسی «سیپلاسپلاس» (++C)، «جاوا» (Java) و «پایتون» (Python) انجام شده است.
پیادهسازی برنامه تشخیص دور اویلری در گراف جهتدار با ++C
// A C++ program to check if a given directed graph is Eulerian or not
#include<iostream>
#include <list>
#define CHARS 26
using namespace std;
// A class that represents an undirected graph
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list<int> *adj; // A dynamic array of adjacency lists
int *in;
public:
// Constructor and destructor
Graph(int V);
~Graph() { delete [] adj; delete [] in; }
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].push_back(w); (in[w])++; }
// Method to check if this graph is Eulerian or not
bool isEulerianCycle();
// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
bool isSC();
// Function to do DFS starting from v. Used in isConnected();
void DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[]);
Graph getTranspose();
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V];
in = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
in[i] = 0;
}
/* This function returns true if the directed graph has a eulerian
cycle, otherwise returns false */
bool Graph::isEulerianCycle()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isSC() == false)
return false;
// Check if in degree and out degree of every vertex is same
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() != in[i])
return false;
return true;
}
// A recursive function to do DFS starting from v
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[v] = true;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list<int>::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i, visited);
}
// Function that returns reverse (or transpose) of this graph
// This function is needed in isSC()
Graph Graph::getTranspose()
{
Graph g(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
list<int>::iterator i;
for(i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
{
g.adj[*i].push_back(v);
(g.in[v])++;
}
}
return g;
}
// This function returns true if all non-zero degree vertices of
// graph are strongly connected (Please refer
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/connectivity-in-a-directed-graph/ )
bool Graph::isSC()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited (For first DFS)
bool visited[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Find the first vertex with non-zero degree
int n;
for (n = 0; n < V; n++)
if (adj[n].size() > 0)
break;
// Do DFS traversal starting from first non zero degrees vertex.
DFSUtil(n, visited);
// If DFS traversal doesn't visit all vertices, then return false.
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() > 0 && visited[i] == false)
return false;
// Create a reversed graph
Graph gr = getTranspose();
// Mark all the vertices as not visited (For second DFS)
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Do DFS for reversed graph starting from first vertex.
// Staring Vertex must be same starting point of first DFS
gr.DFSUtil(n, visited);
// If all vertices are not visited in second DFS, then
// return false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() > 0 && visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
if (g.isEulerianCycle())
cout << "Given directed graph is eulerian n";
else
cout << "Given directed graph is NOT eulerian n";
return 0;پیادهسازی برنامه تشخیص دور اویلری در گراف جهتدار با جاوا
// A Java program to check if a given directed graph is Eulerian or not
// A class that represents an undirected graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency list
class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
private LinkedList<Integer> adj[];//Adjacency List
private int in[]; //maintaining in degree
//Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
in = new int[V];
for (int i=0; i<v; ++i)
{
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
in[i] = 0;
}
}
//Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v,int w)
{
adj[v].add(w);
in[w]++;
}
// A recursive function to print DFS starting from v
void DFSUtil(int v,Boolean visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
int n;
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
Iterator<Integer> i =adj[v].iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
n = i.next();
if (!visited[n])
DFSUtil(n,visited);
}
}
// Function that returns reverse (or transpose) of this graph
Graph getTranspose()
{
Graph g = new Graph(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
Iterator<Integer> i = adj[v].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
g.adj[i.next()].add(v);
(g.in[v])++;
}
}
return g;
}
// The main function that returns true if graph is strongly
// connected
Boolean isSC()
{
// Step 1: Mark all the vertices as not visited (For
// first DFS)
Boolean visited[] = new Boolean[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Step 2: Do DFS traversal starting from the first vertex.
DFSUtil(0, visited);
// If DFS traversal doesn't visit all vertices, then return false.
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
// Step 3: Create a reversed graph
Graph gr = getTranspose();
// Step 4: Mark all the vertices as not visited (For second DFS)
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Step 5: Do DFS for reversed graph starting from first vertex.
// Staring Vertex must be same starting point of first DFS
gr.DFSUtil(0, visited);
// If all vertices are not visited in second DFS, then
// return false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
/* This function returns true if the directed graph has a eulerian
cycle, otherwise returns false */
Boolean isEulerianCycle()
{
// Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected
if (isSC() == false)
return false;
// Check if in degree and out degree of every vertex is same
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() != in[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static void main (String[] args) throws java.lang.Exception
{
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
if (g.isEulerianCycle())
System.out.println("Given directed graph is eulerian ");
else
System.out.println("Given directed graph is NOT eulerian ");
}
}
//This code is contributed by Aakash Hasijaپیادهسازی برنامه تشخیص دوراویلری در گراف جهتدار با پایتون
# A Python program to check if a given
# directed graph is Eulerian or not
from collections import defaultdict
class Graph():
def __init__(self, vertices):
self.V = vertices
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
self.IN = [0] * vertices
def addEdge(self, v, u):
self.graph[v].append(u)
self.IN[u] += 1
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
visited[v] = True
for node in self.graph[v]:
if visited[node] == False:
self.DFSUtil(node, visited)
def getTranspose(self):
gr = Graph(self.V)
for node in range(self.V):
for child in self.graph[node]:
gr.addEdge(child, node)
return gr
def isSC(self):
visited = [False] * self.V
v = 0
for v in range(self.V):
if len(self.graph[v]) > 0:
break
self.DFSUtil(v, visited)
# If DFS traversal doesn't visit all
# vertices, then return false.
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i] == False:
return False
gr = self.getTranspose()
visited = [False] * self.V
gr.DFSUtil(v, visited)
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i] == False:
return False
return True
def isEulerianCycle(self):
# Check if all non-zero degree vertices
# are connected
if self.isSC() == False:
return False
# Check if in degree and out degree of
# every vertex is same
for v in range(self.V):
if len(self.graph[v]) != self.IN[v]:
return False
return True
g = Graph(5);
g.addEdge(1, 0);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
if g.isEulerianCycle():
print "Given directed graph is eulerian";
else:
print "Given directed graph is NOT eulerian";
# This code is contributed by Divyanshu Mehtaخروجی قطعه کدهای بالا به صورت زیر است.
Given directed graph is eulerianپیچیدگی زمانی پیادهسازی بالا از درجه (O(V + E است؛ زیرا الگوریتم کساراجو (O(V + E زمان میبرد. پس از اجرای الگوریتم کساراجو، همه رأسها پیمایش و رأسهای ورودی و خروجی با یکدیگر مقایسه میشوند که این کار از درجه (O(V زمان میبرد.
اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامهنویسی
- آموزش ساختمان دادهها
- مجموعه آموزشهای ساختمان داده و طراحی الگوریتم
- معرفی منابع آموزش ویدئویی هوش مصنوعی به زبان فارسی و انگلیسی
- زبان برنامهنویسی پایتون (Python) — از صفر تا صد
- آموزش ساختمان داده — مجموعه مقالات جامع وبلاگ فرادرس
مجموعه: برنامه نویسی برچسب ها: Eulerian Circuit, برنامه تشخیص دور گراف, تشخیص دور اویلری با ++C, تشخیص دور اویلری با پایتون, تشخیص دور اویلری با جاوا, تشخیص دور در گراف, دور اویلری, دور در گراف, گراف, گراف جهت دار




 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)